News
POGO PINS: Everything You Need to Know About the Design, Development, and Manufacturing Processes
POGO PINS are components used as connectors in the manufacturing and testing of electronic devices. Their most distinctive feature is the spring, which allows for reliable and reusable connections in devices. Essentially, the pins are designed to provide durable electrical connections in applications ranging from test fixtures and battery connectors to a variety of stationary and portable devices.
Structure of POGO PINS
POGO PINS are comprised of three main parts: the plunger, the spring, and the barrel. The plunger is typically made of a highly conductive material, such as gold-plated brass, and it moves within the barrel under the force of the spring to create a stable connection with minimal resistance. The barrel, usually made of a durable material like stainless steel, houses the spring and plunger, ensuring structural integrity.
Design Considerations for POGO PINS
- Electrical Conductivity: The primary function of POGO PINS is to transmit electrical signals, so the materials used must offer excellent conductivity. Gold-plated contacts are often preferred due to their low resistance and high corrosion resistance, ensuring reliable performance over many usage cycles.
- Mechanical Durability: POGO PINS must withstand repeated compression and release. Therefore, the materials used must endure mechanical stress without deforming. Springs are often made from materials like beryllium copper, which allows them to maintain flexibility and strength during repeated use.
- Dimensional Precision: The dimensions of the pins must be extremely precise, down to the micron level, to ensure a perfect fit and optimal contact with the connected surfaces. Any deviation can result in poor connections or mechanical failure.
Manufacturing Process
- Material Selection and Preparation: The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, aligned with the design considerations mentioned above.
- Processing and Shaping: The first step involves manufacturing the three pin components (spring, plunger, barrel) through precise machining processes. Typically, plungers and barrels are produced using CNC machining, which allows for high accuracy and repeatability, while springs are made by carefully winding a metal coil to achieve consistent force characteristics.
- Plating: This is a critical stage, especially for the plunger. The plating process enhances conductivity and resistance to wear and corrosion. Gold plating is done via electrolysis, where the plunger is immersed in a gold solution and an electric current is applied to create a thin, uniform layer of gold on the surface.
- Assembly: Assembling POGO PINS involves placing the spring inside the barrel and inserting the plunger. This process must be executed with high precision to ensure a flawless fit and seamless operation. Automated assembly machines can be used for this purpose.
Quality Control in Pin Manufacturing
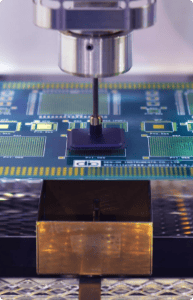
After manufacturing, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive quality control. Each pin must be inspected from all angles to ensure it meets the highest standards. Quality control is performed using automated testing systems, including those for electrical equipment testing.
Key quality control stages may include:
- Dimensional Inspection: The dimensions of each pin are measured using precise tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to ensure they fit their designated slots and maintain optimal contact with the connected surfaces.
- Spring Force Testing: The spring within the pin must exert consistent force throughout multiple usage cycles in the electronic device. This can be checked using specialized equipment that measures the spring force of each POGO PIN to ensure it falls within the required range.
- Electrical Conductivity Testing: After manufacturing, the electrical resistance of each pin is tested. The goal is to produce POGO PINS with low resistance to electrical signals, as high resistance can lead to poor performance or failure in the final application.
- Visual Inspection: Automated systems inspect the final product for defects in components, plating, and assembly. Identifying any visual defect is crucial, as it can affect both performance and durability.
- Lifecycle Testing: To simulate actual use, pins undergo testing where they are exposed to cycles of compression and release. This ensures they can withstand mechanical stresses throughout their intended lifespan.
Potential Challenges in Manufacturing
Although POGO PINS are relatively simple components, consisting of just three parts, manufacturers may still face challenges during production, such as:
- Miniaturization: As electronic devices become smaller, the demand for tiny POGO PINS increases. Producing smaller pins while maintaining the same level of reliability and performance requires advanced manufacturing techniques and precise engineering.
- Material Costs: High-quality materials like gold and beryllium copper can be expensive. Therefore, there is an ongoing challenge of balancing material costs with the need to achieve the best possible results.
- Consistency: Maintaining consistency in mass production is crucial. Variations in the manufacturing process can lead to pins with different electrical and mechanical properties, affecting the final product’s performance.
Applications of POGO PINS
POGO PINS are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Battery Connections: In portable devices, POGO PINS provide reliable connections between the battery and the device’s electrical circuits.
- Testing and Prototyping: POGO PINS play a significant role in testing electronic components and in the production of prototypes.
- Medical Devices: Due to their reliability and precision, POGO PINS are ideal for creating connectors in various medical devices where consistency is paramount.
Innovation and Future Trends
The design, development, and manufacturing processes of POGO PINS are continually evolving to meet the growing demand for smaller components suitable for miniature electronic devices. Modern devices require not only smaller dimensions but also better performance than ever before, necessitating ongoing optimization of manufacturing technologies and cost management in POGO PIN production.
In conclusion, POGO PINS are critical components in many electronic devices, designed to facilitate stable electrical connections in compact structures. Understanding the requirements and characteristics of POGO PIN production, alongside comprehensive quality control, enables reliable, precise, and high-quality manufacturing. By selecting the right materials, meticulous planning, and conducting all the mentioned tests, manufacturers can overcome challenges and produce high-quality POGO PINS for a wide range of applications.
More News Articles